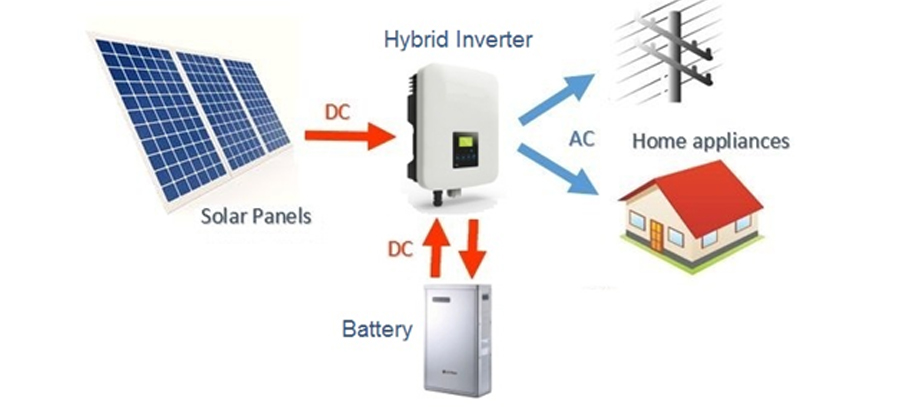
Modern hybrid systems combine solar and battery storage in one and are now available in many different forms and configurations. Due to the decreasing cost of battery storage, systems that are already connected to the electricity grid can start taking advantage of battery storage as well. This means being able to store solar energy that is generated during the day and using it at night. When the stored energy is depleted, the grid is there as a backup, allowing consumers to have the best of both worlds. Hybrid systems are also able to charge the batteries using cheap off-peak electricity (usually after midnight to 6am).
There are also different ways to design hybrid systems but we will keep it simple for now. To learn more about the different hybrid and off-grid power systems refer to our detailed guide to home solar battery systems.
The battery bank. In a hybrid system once the solar power is used by the appliances in your property, any excess power will be sent to the battery bank. Once the battery bank is fully charged, it will stop receiving power from the solar system. The energy from the battery can then be discharged and used to power your home, usually during the peak evening period when the cost of electricity is typically at it’s highest.
The meter and electricity grid. Depending on how your hybrid system is set up and whether your utility allows it, once your batteries are fully charged excess solar power not required by your appliances can be exported to the grid via your meter. When your solar system is not in use, and if you have drained the usable power in your batteries your appliances will then start drawing power from the grid.